
Web 3.0 is the next evolution of the internet, focusing on decentralization, user ownership, and enhanced privacy.
It’s powered by blockchain, cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, decentralized apps (dApps), and the semantic web.
Web 3.0 empowers users with control over their data, enhances online security, eliminates middlemen, and opens up new opportunities in areas like DeFi, NFTs, etc.
Say you wake up one day and realize you own the internet—or at least, the part you use. The apps, the platforms, and even the money you spend online are yours to control. Sounds like a dream, right?
Well, that’s the vision of Web 3.0, often called the “next big thing” in the evolution of the internet. But what is Web 3.0 really about? And why is everyone so excited about it?
It’s not as complicated as it sounds—and by the end of this, you’ll know what Web 3.0 is, how it works, and why it could change your online experience forever.
A Quick Look Back: Web 1.0 and 2.0
To understand Web 3.0, we need to rewind a bit. Internet has evolving in three big stages:
Web 1.0 – The Static Web
Web 1.0 was the internet’s baby phase. It started in the 1990s and was mostly read-only. Imagine a giant library where you could look up information but couldn’t interact much.
Websites were simple, text-heavy, and not very user-friendly. You could read stuff, but that was about it. It was kind of a digital brochure—useful, but not interactive.
Web 2.0 – The Social Web
Enter Web 2.0 in the mid-2000s, and everything changed.
Suddenly, you weren’t just reading the internet; you were participating. Social media platforms like Facebook and YouTube came along. You could post, comment, share, and create content. Apps became smarter and more interactive.
Companies like Google and Amazon made the internet a personalized experience. But there was a catch: these platforms owned your data. They profited from it, and you didn’t have much control over how it was used.
And that brings us to where we are now—on the edge of Web 3.0.
So, What Is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is the next step in the evolution of the internet. At its core, it’s about decentralization and giving control back to users.
Instead of big companies like Facebook or Google owning and controlling everything, Web 3.0 aims to let people own their online identities, data, and assets.
Here’s a simple way to think about it:
- In Web 1.0, you could only read the web.
- In Web 2.0, you could read and write (interact with it).
- In Web 3.0, you can read, write, and own parts of the web.
Sounds cool, right? But how does it actually work? Let’s break it down.
The Building Blocks of Web 3.0
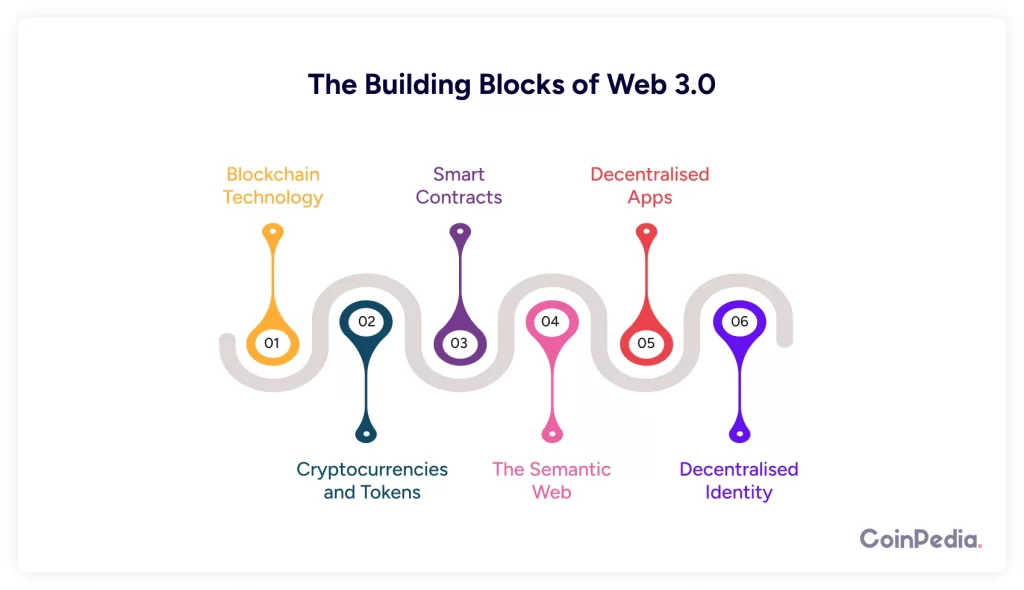
Web 3.0 isn’t just a single thing—it’s made up of several technologies working together. Here are the main ones:
1. Blockchain Technology
At the heart of Web 3.0 is blockchain. If you’ve heard of Bitcoin or Ethereum, you’ve already encountered blockchain. It’s a way to store data securely and transparently without needing a central authority.
We already know it is like a digital ledger that everyone can see, but no one can tamper with. In Web 3.0, blockchain powers everything from decentralized apps (dApps) to digital currencies.
2. Cryptocurrencies and Tokens
In Web 3.0, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are more than just digital money. They’re also tools for ownership.
For example, you might earn tokens for contributing to a platform. These tokens could give you voting rights or a share of the platform’s profits.
3. Smart Contracts
These are self-executing programs that run on blockchain. They work like contracts in the real world but without middlemen.
For example, if you rent a house through a smart contract, the payment and key transfer happen automatically once conditions are met. No need for a landlord or agent.
4. Decentralized Apps (dApps)
Unlike regular apps, dApps run on blockchain. They’re open-source and don’t rely on a central server. This means no single entity controls them, and they’re more resistant to censorship.
5. The Semantic Web
Web 3.0 isn’t just about ownership; it’s also about smarter information. The semantic web aims to make data on the internet more connected and meaningful. It’s like teaching the internet to understand context.
For example, instead of just showing you search results, Web 3.0 could give you answers tailored to your exact needs.
6. Decentralized Identity
In Web 3.0, you control your online identity. Instead of signing up for every app with your email or social media account, you could use a decentralized identity that’s tied to you, not a company. This keeps your data private and secure.
Why Does Web 3.0 Matter?
Okay, so now you know what Web 3.0 is made of. But why should you care? Here are some of the biggest reasons:
1. Ownership and Control
In Web 3.0, you own your data and assets. Whether it’s the content you create or the money you earn, you’re in charge. No more relying on platforms that can change the rules or lock you out.
2. Privacy and Security
Because Web 3.0 is decentralized, your data isn’t stored on a single server. This makes it much harder for hackers to steal it. Plus, you decide who gets access to your information.
3. No Middlemen
Web 3.0 cuts out the middlemen. Whether it’s banks, app stores, or ad companies, you don’t need third parties taking a cut or controlling the process.
4. Censorship Resistance
In Web 3.0, no single company or government can censor or shut down platforms. This is especially important for people in countries with strict online controls.
5. New Opportunities
Web 3.0 opens up a world of possibilities. You could earn money by participating in online communities, trade digital assets, or even create your own decentralized app.
Examples of Web 3.0 in Action
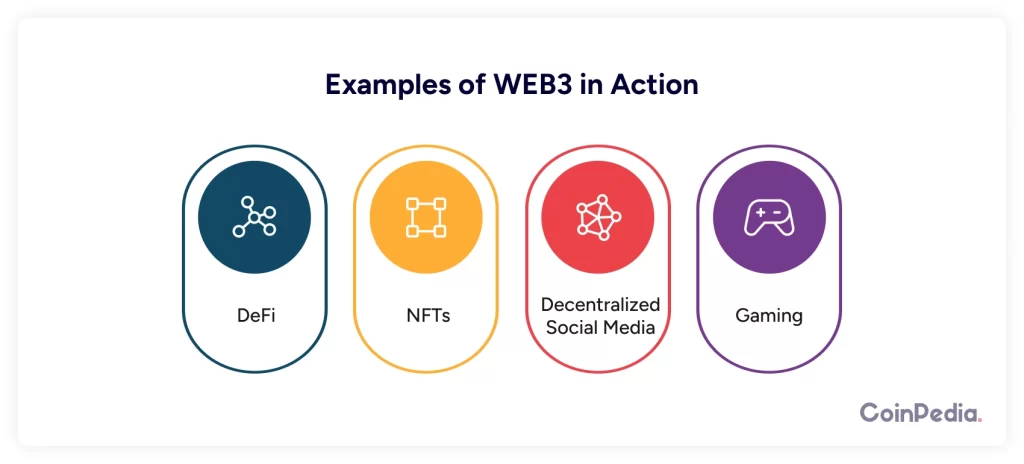
Still wondering what Web 3.0 looks like in real life? Here are a few examples:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Platforms like Aave and Uniswap let you lend, borrow, or trade cryptocurrencies without a bank.
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): These are unique digital assets that can represent anything from art to music. You own them, and they can’t be copied.
- Decentralized Social Media: Imagine a social media platform where you own your posts and can earn money from them. Platforms like Lens Protocol are already working on this.
- Gaming: Play-to-earn games like Axie Infinity reward players with cryptocurrency. You can even own in-game assets and trade them.
Challenges of Web 3.0
Of course, Web 3.0 isn’t perfect.
Here are some of the challenges it faces:
- Complexity: Right now, Web 3.0 can be hard to use for non-tech-savvy people. Wallets, keys, and tokens can feel overwhelming.
- Scalability: Blockchain networks can be slow and expensive, especially during high demand. Developers are working on solutions, but it’s still a hurdle.
- Regulation: Governments are still figuring out how to regulate Web 3.0 technologies, which could create uncertainty.
- Adoption: For Web 3.0 to succeed, more people need to use it. This will take time and education.
The Future of Web 3.0
Despite the challenges, Web 3.0 has enormous potential. Imagine a world where you’re not just a user of the internet but a co-owner. A world where your data works for you, not for tech giants. A world where online communities thrive without interference or exploitation.
We’re still in the early days of Web 3.0, but the foundation is being built. Developers, entrepreneurs, and innovators are creating tools and platforms that could reshape how we interact online.
It’s an exciting time—and you’re part of it just by learning and exploring.
Final Thoughts
So, what is Web 3.0? It’s not just a new version of the internet; it’s a new way of thinking about ownership, control, and connection. It’s about empowering individuals and creating a more open, fair, and secure online world.
Does this mean you need to dive into blockchain or start buying crypto right now? Not necessarily. But understanding Web 3.0 puts you ahead
FAQs
Web 3.0 is a decentralized internet where users own data and assets, unlike Web 2.0, which is dominated by centralized platforms.
Blockchain ensures secure, transparent data storage and enables decentralized apps, digital ownership, and smart contracts in Web 3.0.
Examples include decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, play-to-earn games, and decentralized social media platforms.
Challenges include complexity for users, scalability issues, unclear regulations, and the need for widespread adoption.
We'd Love to Hear Your Thoughts on This Article!
Was this writing helpful?
 Yes
Yes  No
No
Trust with CoinPedia:
CoinPedia has been delivering accurate and timely cryptocurrency and blockchain updates since 2017. All content is created by our expert panel of analysts and journalists, following strict Editorial Guidelines based on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Every article is fact-checked against reputable sources to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability. Our review policy guarantees unbiased evaluations when recommending exchanges, platforms, or tools. We strive to provide timely updates about everything crypto & blockchain, right from startups to industry majors.
Investment Disclaimer:
All opinions and insights shared represent the author's own views on current market conditions. Please do your own research before making investment decisions. Neither the writer nor the publication assumes responsibility for your financial choices.
Sponsored and Advertisements:
Sponsored content and affiliate links may appear on our site. Advertisements are marked clearly, and our editorial content remains entirely independent from our ad partners.




