
If you’ve spent any time in the crypto world, you’ve probably heard of Polygon (MATIC). But why does it matter? Well, imagine you’re using Ethereum, excited about DeFi apps, NFTs, or just transferring tokens. Suddenly, you realize transactions are slow and gas fees are sky-high.
That’s where Polygon steps in. It makes transactions faster and cheaper, without compromising Ethereum’s security. It’s like taking the highway instead of being stuck in traffic.
So, let’s break it down and understand what makes Polygon a game-changer in crypto.
1. What is Polygon?
Think of Polygon as a booster for Ethereum. Ethereum is powerful, but it has problems—it’s slow and expensive. Polygon fixes that by working alongside Ethereum rather than replacing it.
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution. That means it helps Ethereum handle more transactions without overloading the network. It does this by processing transactions off-chain (outside Ethereum’s main network) and then sending the final result back to Ethereum.
Simple Example:
Imagine a busy highway (Ethereum). It gets jammed during rush hour, and every car (transaction) moves slowly. Now, Polygon builds side roads where cars can move faster and rejoin the highway only when necessary. The result? Lower traffic, faster speeds, and cheaper tolls (gas fees).
Polygon isn’t a single technology. It’s an entire ecosystem of solutions that improve blockchain performance. The most well-known product is Polygon PoS (Proof-of-Stake), but they also have advanced tech like Polygon zkEVM and Polygon Supernets (more on these later).
2. History of Polygon: From MATIC to Multi-Chain Powerhouse
Polygon wasn’t always called Polygon. It started in 2017 as Matic Network, founded by three Indian developers—Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, and Anurag Arjun. Back then, Ethereum’s scalability issues were becoming a major problem. The team saw an opportunity to fix it.
In 2020, they rebranded from Matic Network to Polygon to reflect their expanded vision—not just scaling Ethereum, but creating an interconnected blockchain network (like an “Internet of Blockchains”).
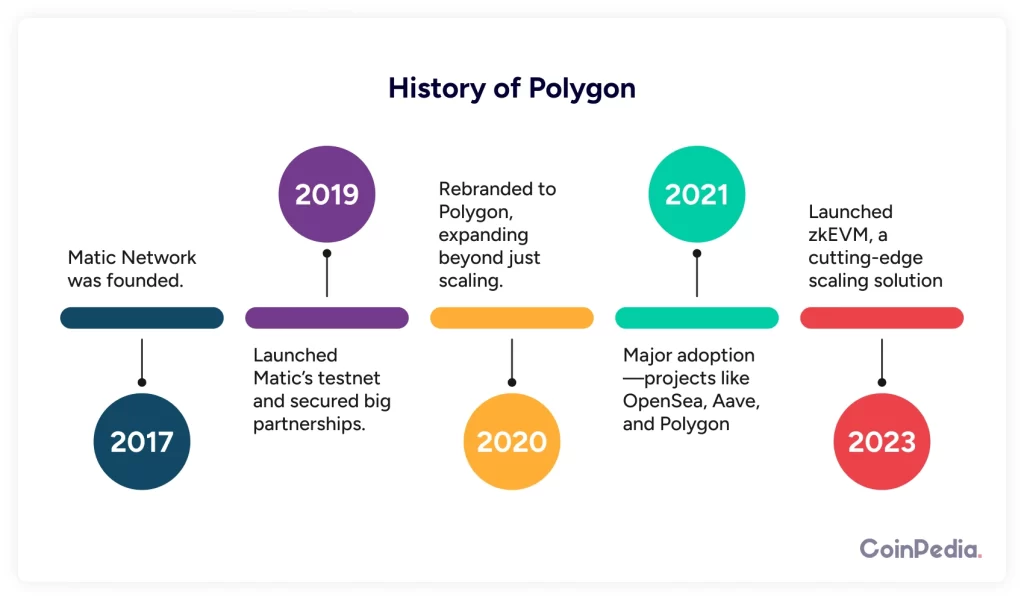
Key milestones:
- 2017: Matic Network was founded.
- 2019: Launched Matic’s testnet and secured big partnerships.
- 2020: Rebranded to Polygon, expanding beyond just scaling.
- 2021: Major adoption—projects like OpenSea, Aave, and Decentraland started using Polygon.
- 2023: Launched zkEVM, a cutting-edge scaling solution.
Today, Polygon is one of the biggest names in the crypto space. It’s backed by investors like Mark Cuban and works with companies like Disney, Starbucks, and Reddit.
3. How Does Polygon Work?
Polygon uses different scaling solutions to make transactions faster and cheaper. The most popular one is Polygon PoS (Proof-of-Stake chain).
How Polygon PoS Works:
- Transactions happen off Ethereum. Instead of processing everything on Ethereum, transactions occur on Polygon’s own network.
- Validators confirm transactions. These are special nodes that verify transactions, ensuring security and efficiency.
- Final results go back to Ethereum. Once transactions are bundled and confirmed, they are sent back to Ethereum’s blockchain.
Polygon also has advanced solutions like zkEVM (zero-knowledge rollups) and Optimistic rollups, which provide even better performance.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Polygon
Advantages of Polygon:
- Super Low Fees: Ethereum gas fees can be $20 or more per transaction. On Polygon? Often less than a cent!
- Fast Transactions: Instead of waiting minutes (or hours) on Ethereum, Polygon completes transactions in seconds.
- Strong Security: It uses Ethereum’s security but adds extra protection through validators.
- Wide Adoption: Over 37,000 dApps (decentralized apps) run on Polygon, including OpenSea, Aave, and Uniswap.
- Eco-Friendly: Unlike Bitcoin and Ethereum (which use energy-intensive mining), Polygon’s Proof-of-Stake system is much greener.
Disadvantages of Polygon:
- Not as Decentralized as Ethereum: Polygon relies on a set of validators, which means it’s not as decentralized as Ethereum itself.
- Competition from Other Layer-2s: Solutions like Arbitrum and Optimism are also trying to solve Ethereum’s problems.
- Security Risks: Since transactions happen off-chain, some argue it could be less secure than Ethereum.
5. Real-World Use Cases of Polygon
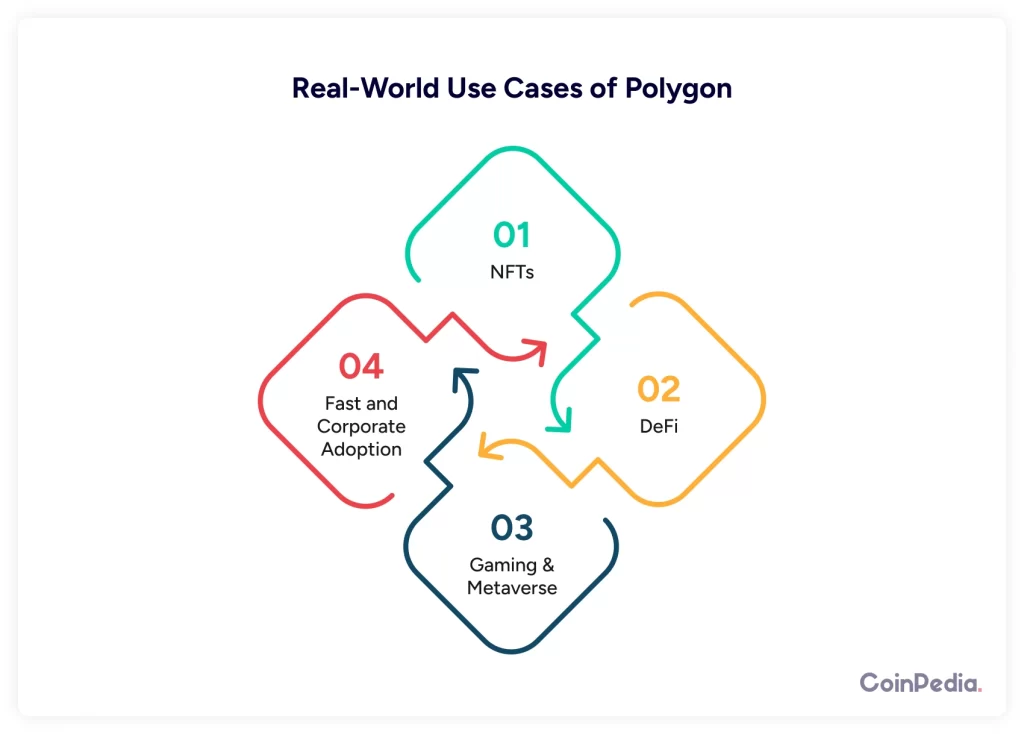
Polygon isn’t just a theory—it’s actively used in the real world. Here are some big ways it’s making an impact:
- NFTs: OpenSea (the largest NFT marketplace) allows users to trade NFTs on Polygon with zero gas fees.
- DeFi: Aave, one of the biggest lending platforms, offers cheaper loans and transactions on Polygon.
- Gaming & Metaverse: Decentraland and Sandbox use Polygon for fast and cheap in-game transactions.
Corporate Adoption: Starbucks, Nike, and Reddit are using Polygon for digital collectibles and rewards programs.
6. Future of Polygon: What’s Next?
Polygon isn’t stopping anytime soon. They are constantly upgrading to stay ahead in the crypto world.
Some major future developments:
- Polygon zkEVM (Zero-Knowledge Rollups): This will make transactions even faster while maintaining Ethereum-level security.
- Polygon 2.0: A complete overhaul that aims to turn Polygon into a true multi-chain network, similar to Polkadot or Cosmos.
- Bigger Partnerships: With companies like Google Cloud and Disney already on board, expect more big names to join.
- More DeFi & NFT Growth: As gas fees on Ethereum remain high, more projects will move to Polygon for cheaper alternatives.
Will Polygon Survive Long-Term?
While crypto is unpredictable, Polygon has built a strong foundation. With its growing adoption and continuous upgrades, it is well-positioned to remain a major player in blockchain scaling.
Final Thoughts: Is Polygon the Future?
Polygon has revolutionized how Ethereum transactions work. It has made crypto more accessible by reducing fees and increasing speed. Whether you’re into DeFi, NFTs, or gaming, Polygon offers a better experience than using Ethereum alone.That said, competition is growing. New layer-2 solutions like Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync are challenging Polygon. But with its continuous innovation and strong partnerships, Polygon still stands out as one of the best solutions for scaling Ethereum.
10. FAQs
The Polygon’s PoS element is the one which complements Ethereum’s decentralized security.
Polygon is a Layer 2 blockchain which helps Ethereum with its scalability!
It uses an efficient and low-energy Proof of Stake model to secure its network and achieve safety.
We'd Love to Hear Your Thoughts on This Article!
Was this writing helpful?
 Yes
Yes  No
No
Trust with CoinPedia:
CoinPedia has been delivering accurate and timely cryptocurrency and blockchain updates since 2017. All content is created by our expert panel of analysts and journalists, following strict Editorial Guidelines based on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Every article is fact-checked against reputable sources to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability. Our review policy guarantees unbiased evaluations when recommending exchanges, platforms, or tools. We strive to provide timely updates about everything crypto & blockchain, right from startups to industry majors.
Investment Disclaimer:
All opinions and insights shared represent the author's own views on current market conditions. Please do your own research before making investment decisions. Neither the writer nor the publication assumes responsibility for your financial choices.
Sponsored and Advertisements:
Sponsored content and affiliate links may appear on our site. Advertisements are marked clearly, and our editorial content remains entirely independent from our ad partners.




