
Imagine a world where you don’t need banks to send money, lawyers to make contracts, or middlemen to control your digital life. That’s the world Ethereum is building. It’s not just another cryptocurrency; it’s a whole new way to run the internet. Let’s dive deep into Ethereum, understand how it works, and where it’s headed.
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that allows developers to build applications without relying on a central authority. Unlike Bitcoin, which is mainly a digital currency, Ethereum is more like a giant, global computer that runs programs known as smart contracts.
Think of Ethereum as an app store. But instead of Apple or Google controlling which apps can run, Ethereum is open to everyone. No single company or government can shut it down. This makes it a game-changer for finance, gaming, real estate, and many other industries.
What Makes Ethereum Special?
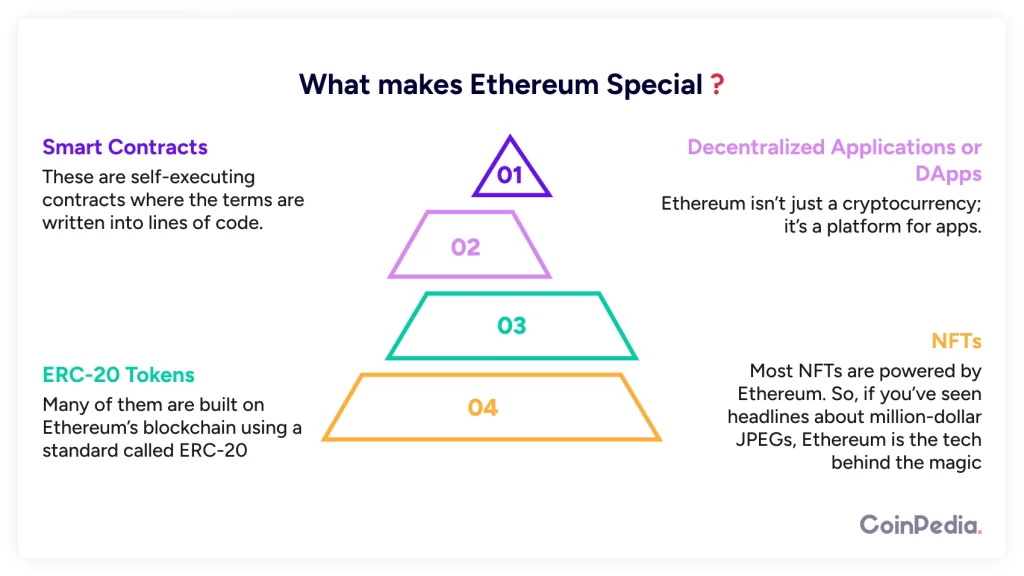
- Smart Contracts – Self-executing programs that run exactly as coded. No need for a third party.
- Decentralized – No single entity controls Ethereum. It’s powered by thousands of computers worldwide.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) – A global, decentralized computer that runs all Ethereum applications.
Let’s break this down further with an example: Imagine you want to bet with a friend on a football game. Normally, you’d need a trusted third party to hold the money and distribute it to the winner. With Ethereum, a smart contract can handle everything automatically. No need to trust a person or a company – the code takes care of it.
History of Ethereum
Ethereum was created by Vitalik Buterin, a young programmer who saw the limitations of Bitcoin. While Bitcoin was great for sending money, it wasn’t flexible enough to handle complex applications. In 2013, Buterin proposed Ethereum as a new blockchain that could run any program.
Ethereum officially launched in 2015, and it quickly became the second-largest cryptocurrency after Bitcoin. Over the years, it has gone through multiple upgrades, improving security, scalability, and efficiency.
Key Milestones:
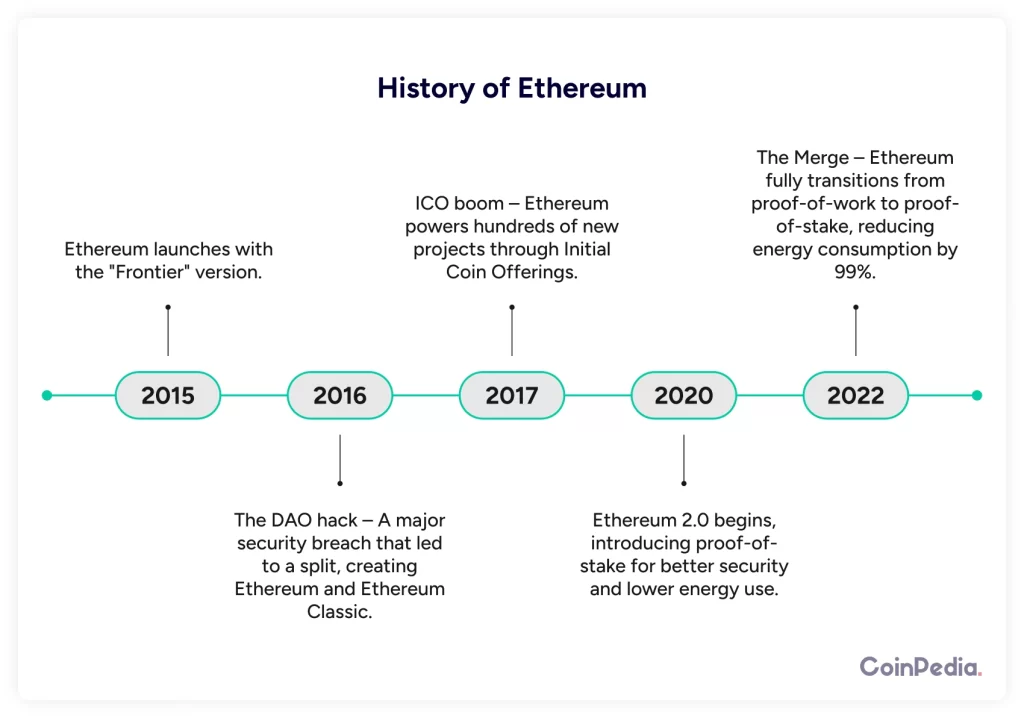
- 2015: Ethereum launches with the “Frontier” version.
- 2016: The DAO hack – A major security breach that led to a split, creating Ethereum and Ethereum Classic.
- 2017: ICO boom – Ethereum powers hundreds of new projects through Initial Coin Offerings.
- 2020: Ethereum 2.0 begins, introducing proof-of-stake for better security and lower energy use.
- 2022: The Merge – Ethereum fully transitions from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, reducing energy consumption by 99%.
Ethereum is still evolving, and its future looks even more promising.
How Does Ethereum Work?
Ethereum runs on a blockchain – a digital ledger that records all transactions. But it does much more than just store payments. It can run smart contracts, which are self-executing pieces of code.
The Key Parts of Ethereum:
- Blockchain – The public ledger where all transactions and smart contracts are stored.
- Smart Contracts – Small programs that run on Ethereum and execute automatically.
- Ether (ETH) – The native cryptocurrency of Ethereum, used to pay for transactions and fees.
- Nodes & Validators – Computers that help run the Ethereum network and keep it secure.
Let’s take an example: Suppose you rent an apartment. Instead of signing a paper contract, you can use a smart contract on Ethereum. Once you send the deposit in ETH, the contract automatically grants you access to the apartment. If you don’t pay rent on time, access is revoked. No need for a landlord to intervene – the contract does everything.
This is why Ethereum is so powerful. It removes the need for middlemen in everyday transactions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ethereum
Ethereum is revolutionary, but it’s not perfect. Let’s look at both sides of the coin.
Advantages:
- Decentralization – No single company or government controls Ethereum.
- Smart Contracts – Automate transactions without intermediaries.
- Security – Transactions are verified and recorded on the blockchain.
- Continuous Innovation – Ethereum is always upgrading to improve performance.
Disadvantages:
- High Gas Fees – Transactions can be expensive during peak times.
- Scalability Issues – Ethereum can slow down when too many people use it.
- Complexity – Smart contracts can be difficult to program correctly, leading to hacks.
The good news? Ethereum developers are working on solutions like Layer 2 scaling (Optimism, Arbitrum) and sharding to make transactions cheaper and faster.
Future of Ethereum
Ethereum has already come a long way, but the best is yet to come. Here are some key developments on the horizon:
- Ethereum 2.0 Completion – Ethereum is shifting to a more scalable network with lower fees.
- Layer 2 Solutions – Networks like Polygon and Optimism will make transactions cheaper and faster.
- Real-World Adoption – More companies and governments are experimenting with Ethereum.
- DeFi & NFTs – Decentralized finance and NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are growing industries powered by Ethereum.

The big question is: Will Ethereum dominate the digital economy? Only time will tell, but it’s clear that Ethereum is here to stay.
How Safe is Solana Compared to Ethereum?
Solana is often compared to Ethereum because it’s faster and has lower fees. But is it safer?
Solana’s Strengths:
- High Speed – Can process over 65,000 transactions per second.
- Low Fees – Transactions cost less than a penny.
Solana’s Weaknesses:
- Centralization Concerns – Solana relies on fewer nodes, making it less decentralized than Ethereum.
- Network Outages – Solana has suffered multiple outages, which raises reliability concerns.
While Solana is a promising competitor, Ethereum remains the most secure and widely adopted blockchain for smart contracts.
Conclusion
Ethereum is changing the way we interact with money, contracts, and even the internet. From smart contracts to decentralized apps, it’s a powerful tool that removes middlemen and gives control back to users.
But it’s not without challenges – high fees, scalability issues, and competition from blockchains like Solana. However, with ongoing upgrades and innovations, Ethereum is set to remain a leader in the blockchain space.
So, the next time you hear about Ethereum, you’ll know it’s not just a cryptocurrency. It’s the foundation of a new, decentralized world. And we’re just getting started!
FAQs
Ethereum is a blockchain platform that supports decentralized apps (DApps) and smart contracts, using Ether (ETH) as its currency.
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements where terms are written in code, automating processes without intermediaries.
While Bitcoin is digital money, Ethereum is a blockchain platform for decentralized apps, smart contracts, and digital assets like NFTs.
Ethereum 2.0 is an upgrade to Ethereum’s blockchain, shifting to Proof of Stake (PoS) for energy efficiency, scalability, and security improvements.
We'd Love to Hear Your Thoughts on This Article!
Was this writing helpful?
 Yes
Yes  No
No
Trust with CoinPedia:
CoinPedia has been delivering accurate and timely cryptocurrency and blockchain updates since 2017. All content is created by our expert panel of analysts and journalists, following strict Editorial Guidelines based on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Every article is fact-checked against reputable sources to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability. Our review policy guarantees unbiased evaluations when recommending exchanges, platforms, or tools. We strive to provide timely updates about everything crypto & blockchain, right from startups to industry majors.
Investment Disclaimer:
All opinions and insights shared represent the author's own views on current market conditions. Please do your own research before making investment decisions. Neither the writer nor the publication assumes responsibility for your financial choices.
Sponsored and Advertisements:
Sponsored content and affiliate links may appear on our site. Advertisements are marked clearly, and our editorial content remains entirely independent from our ad partners.




